Engaging in regular cardio exercise offers numerous health benefits, including improved heart health, increased lung capacity, reduced risk of chronic diseases (e.g., heart disease, diabetes), enhanced mood, better sleep quality, and increased energy levels. These benefits are more than enough to make cardio any human being’s top priority to make them healthier but just like everything else in life, cardio is also not good if you are doing it too much. But, how much cardio is too much to affect your health in an adverse way? To know the answer, continue reading the article where we have discussed about bad effects of overtraining cardio and how to know – how much cardio is too much?!
Negative Effects of Overtraining Cardio!
While cardio exercises are generally beneficial for overall health and fitness, overtraining in this area can have negative effects on the body. Here are some potential bad effects of overtraining cardio exercises that you should know first before jumping into the ways of how to know – how much cardio is too much? Because, after knowing these bad effects of overtraining cardio, you can also realise whether you are involving your body in too much cardio or not! So, let’s get them started.
Increased risk of injury
Overtraining cardio can lead to excessive wear and tear on the muscles, joints, and connective tissues, increasing the risk of injuries such as strains, sprains, stress fractures, and tendonitis.

Decreased immune function
Intense and prolonged cardio workouts without adequate rest and recovery can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and slower recovery times.

Hormonal imbalances
Overtraining can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in the body. Excessive cardio exercise can increase the production of stress hormones like cortisol, while decreasing levels of reproductive hormones such as testosterone and estrogen. This can lead to a range of issues including decreased libido, disrupted menstrual cycles in women, and muscle loss.

Plateau or decline in performance
Overtraining cardio can hinder progress rather than enhance it. When the body is pushed beyond its limits without enough time for recovery, performance gains can stagnate or even decline. This can be frustrating for individuals who are aiming to improve their cardiovascular fitness.
Don’t Miss: Workout Plateau: 5 Proven Methods To Overcome it!
Chronic fatigue and mood disturbances
Overtraining can lead to chronic fatigue, excessive tiredness, and persistent muscle soreness. It can also cause mood disturbances such as irritability, depression, and difficulty sleeping, which can have a negative impact on overall well-being.
Decreased muscle mass
Excessive cardio exercises, especially without adequate strength training, can lead to muscle catabolism (breakdown) and reduced muscle mass. This can result in a slower metabolic rate and a less toned appearance.

Nutritional deficiencies
Overtraining can increase the body’s demand for nutrients and energy. Failing to meet these increased requirements through a well-balanced diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies, which may impact overall health and performance.
It’s important to note that these effects may vary depending on individual factors such as fitness level, training history, and overall health. Nevertheless, if you find any of these abovementioned negative effects of overtraining hampering your health then it’s time to strike a balance between cardio exercise, strength training, rest, diet and recovery and all these things should be in optimum amount because from over dieting to overtraining – anything too much is bad for health in several ways.
So, How Much Cardio Is Too Much, Really?!
To determine how much cardio is too much for you, here are the best ways to gauge your exercise intensity and assess your body’s response.
Monitor your heart rate
Tracking your heart rate during cardio workouts can provide valuable information about exercise intensity. Use a heart rate monitor or check your pulse manually to ensure you’re within a target heart rate zone. Exceeding your maximum heart rate (220 minus your age) for prolonged periods may indicate that you’re pushing yourself too hard.
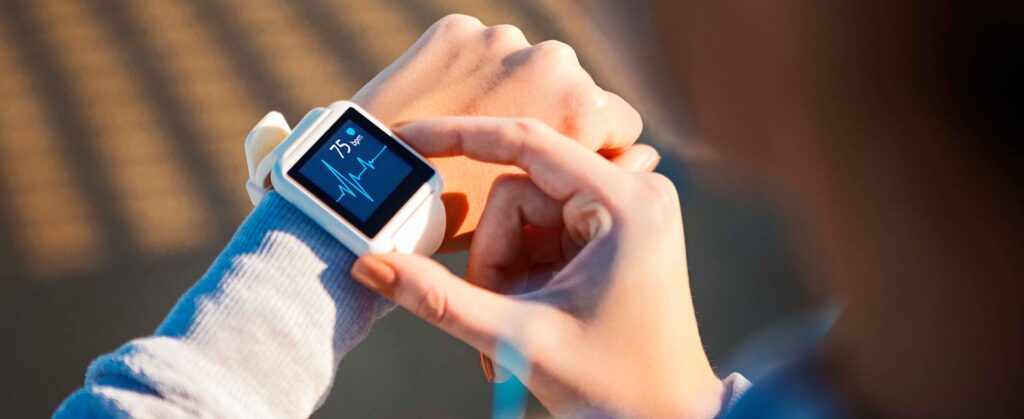

Pay attention to perceived exertion
Rate your perceived exertion on a scale of 1 to 10, with 1 being very light and 10 being maximal effort. If you consistently find yourself rating your exertion level at 8 or above during cardio sessions, it may be an indicator that you’re pushing yourself too much.
Consider your recovery
Notice how well you recover between cardio sessions. If you find that you’re constantly fatigued, experiencing prolonged muscle soreness, or struggling to perform at your usual level, it may be a sign that you need to scale back your cardio or allow for more rest and recovery.
Also Read: 10 Highest Omega-3 Foods That You Shouldn’t Avoid!
Watch for signs of overtraining
Look out for symptoms of overtraining, such as persistent fatigue, decreased performance, increased injuries, disrupted sleep patterns, mood changes, and decreased motivation – all of them we have already explained in this article. If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to reduce your cardio volume and intensity and prioritize rest and recovery.
Assess your overall health and goals
Consider your current health status, fitness level, and specific goals. If you’re recovering from an injury or have underlying health conditions, you may need to modify your cardio routine accordingly. Additionally, if your goals involve muscle gain or strength improvement, you should ensure that your cardio doesn’t interfere with your strength training program.

Seek professional guidance
Consulting with a healthcare or fitness professional, such as a doctor, exercise physiologist, or certified personal trainer, can provide valuable insights into how much cardio is appropriate for you. They can assess your individual circumstances and provide personalized recommendations based on your goals, health status, and fitness level.
So, How Much Cardio is Optimum?
It is generally recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity cardio exercise per week for optimal health and fitness. However, it is for young adults. For older persons, it may vary depending on factors like fitness level, training history and overall health. In that case, seeking professionals is the best option as we already said.

Remember, finding the right balance is key. Gradually increase your cardio volume and intensity over time, listen to your body, and be open to adjusting your routine as needed to ensure that you’re getting the benefits of cardio exercise without overdoing it. Hopefully, we have cleared all your confusions regarding how much cardio is too much?! If it is really so then don’t hesitate to express your valuable thoughts in the comment section below. Thanks for visiting and appreciating our work.
