Coke Zero, a zero-calorie soft drink introduced as a sugar-free alternative, has garnered both popularity and scrutiny since its inception. Marketed as a beverage that delivers the familiar taste of Coca-Cola without the caloric content, Coke Zero has become a go-to choice for those aiming to reduce sugar intake or manage their weight. However, the question lingers: Is Coke Zero bad for you? In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the Coke Zero ingredients, potential health impacts, and controversies surrounding Coke Zero to uncover the truth about its impact on health so that you can get to know the answer to the question: Is Coke Zero Bad for you? Let’s get started.

Coke Zero Ingredients: What’s Inside?
To understand the potential effects of Coke Zero on health, it’s essential to examine its ingredients.
- Carbonated Water: The primary ingredient in Coke Zero, carbonated water provides the effervescence characteristic of sodas.
- Caramel Color: Caramel color is added for visual appeal. It is a common food additive used in various beverages and foods.
- Phosphoric Acid: Phosphoric acid contributes to the soda’s tangy flavor. It is also found in traditional Coca-Cola and is known for its acidic properties.
- Aspartame: Aspartame is a low-calorie artificial sweetener used to provide sweetness without the caloric content associated with sugar.
- Potassium Benzoate (Preservative): Potassium benzoate is a preservative added to enhance the shelf life of the beverage.
- Natural Flavors: Natural flavors are included to replicate the taste of regular Coca-Cola.
- Potassium Citrate: Potassium citrate is added to regulate acidity and act as a source of potassium.
- Acesulfame Potassium: Acesulfame potassium is another artificial sweetener used to enhance sweetness without calories.
Don’t Miss: Coke Zero Nutrition Facts: A Comprehensive Overview

The Controversy Surrounding Aspartame
Aspartame, the key artificial sweetener used in Coke Zero, has been the subject of not only extensive research and scrutiny but also controversy and debate. While regulatory authorities worldwide, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), and the World Health Organization (WHO), have deemed aspartame safe for consumption within established limits, some concerns and controversial claims have been raised. Let’s take a look into the controversies and negative effects (if any) associated with aspartame in Coke Zero.
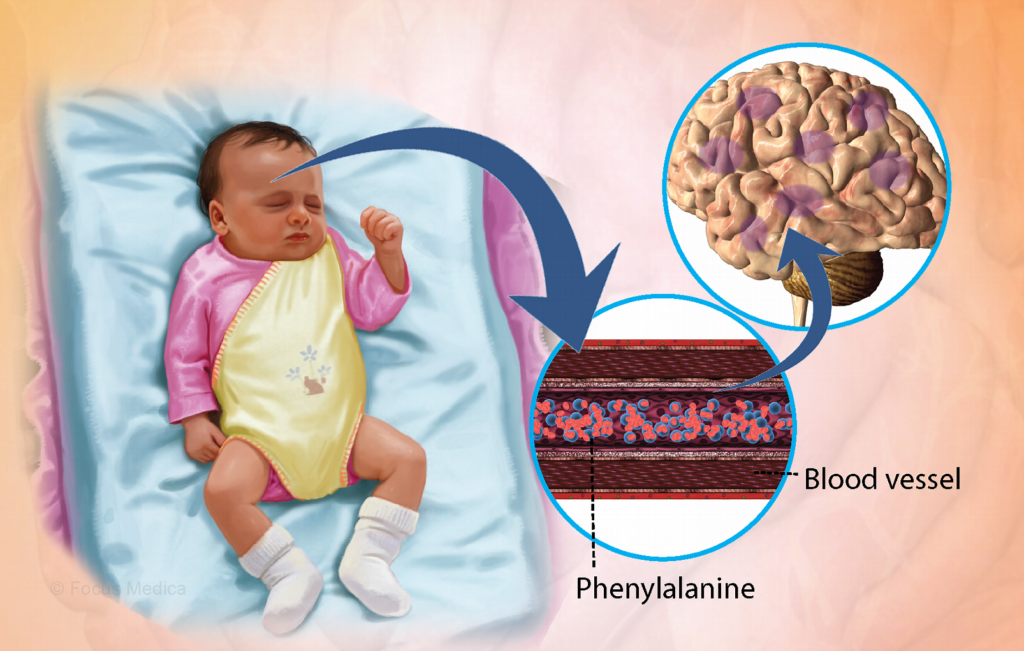
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Individuals with a rare genetic disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU) lack the enzyme needed to metabolize phenylalanine, a component of aspartame. Phenylalanine can accumulate in the blood, leading to intellectual disabilities and other health issues in individuals with PKU. For this reason, products containing aspartame carry a warning for individuals with PKU to avoid them.
Migraines and Headaches
Some individuals report experiencing headaches or migraines after consuming aspartame-containing products, including Coke Zero. However, the scientific evidence supporting a causal relationship between aspartame and headaches is inconsistent. Many studies have failed to establish a direct link, and individual responses can vary.

Potential Impact on Mental Health
Anecdotal reports and some studies have suggested a potential association between aspartame consumption and adverse effects on mood or mental health. However, robust scientific evidence supporting a causal link remains inconclusive. As with headaches, individual responses can vary, and factors beyond aspartame consumption may contribute to reported effects.

Cancer Concerns
Aspartame has been the subject of numerous studies assessing its potential link to cancer. The scientific consensus, including evaluations by regulatory agencies, is that aspartame is safe for consumption within established limits. However, controversies persist, with some studies raising questions about its safety. The majority of research, including large-scale reviews, has not found compelling evidence supporting a carcinogenic effect of aspartame.

Weight Gain and Metabolic Responses
Paradoxically, artificial sweeteners like aspartame in Coke Zero are often chosen to help manage weight due to their lack of calories. However, some studies have suggested that artificial sweeteners may influence metabolic responses in a way that could lead to weight gain over time. The mechanisms behind these potential effects are not fully understood, and further research is needed to elucidate the complex interactions.

Digestive Distress
In some cases, individuals have reported digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, or abdominal discomfort, after consuming aspartame-containing products. However, these effects are generally mild and not consistently observed in research studies.

Cognitive Function
Aspartame contains phenylalanine, an amino acid that is a precursor to neurotransmitters in the brain. While phenylalanine is essential for brain function, concerns have been raised about potential effects on cognitive function. Existing research has not provided clear evidence of adverse cognitive effects at typical levels of aspartame consumption.

Perceived Sweetness and Sugar Cravings
Some studies have suggested that consuming artificial sweeteners, including aspartame, may lead to an increased preference for sweet tastes and potentially influence sugar cravings. However, the overall impact on dietary habits varies among individuals, and more research is needed to fully understand these behavioral aspects.

Positive Health Impacts of Coke Zero
Enough with the controversies and debates on potential negative impact of Coke Zero. Now, it’s time to look into the proven positive impacts of Coke Zero on health so that you can get a rough idea of your question: Is Coke Zero bad for you?
Calorie Reduction
One of the primary reasons individuals opt for Coke Zero is its zero-calorie content. This can be beneficial for those aiming to reduce overall calorie intake, manage their weight, or support weight loss efforts. By choosing a zero-calorie beverage, individuals can enjoy a soda-like experience without the added calories found in regular sugary sodas.

Blood Sugar Control
Coke Zero is free from sugars, making it a suitable option for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage blood sugar levels. Unlike sugary sodas, Coke Zero does not contribute to spikes in blood sugar, making it a safer choice for individuals who need to monitor their glucose levels.

Dental Health
Unlike traditional sugary sodas, Coke Zero does not contribute to tooth decay. The absence of sugars in Coke Zero means there is no fuel for the bacteria in the mouth to produce acids that can erode dental enamel. While Coke Zero is acidic due to the presence of phosphoric acid, it is less likely to cause dental issues compared to sugary counterparts.

Weight Management Support
For individuals aiming to manage their weight or make healthier beverage choices, Coke Zero can be a tool to reduce overall caloric intake as it is already discussed. This can contribute to a balanced and calorie-conscious diet, supporting weight management goals without sacrificing the enjoyment of a carbonated beverage.
Hydration
Coke Zero is primarily composed of carbonated water, contributing to overall hydration. While it’s important to note that water remains the healthiest and most hydrating choice, Coke Zero can be part of a hydration strategy for those who enjoy the carbonated taste without the additional calories and sugars.

Choice for Individuals with Dietary Restrictions
Individuals with dietary restrictions or those who need to limit their sugar intake may find Coke Zero to be a suitable alternative. It provides a sweetened beverage option without the sugars that may be restricted for health reasons.
Caffeine Content
Coke Zero contains caffeine, which can have stimulating effects. For those who enjoy the boost of caffeine without the calories found in regular sodas or coffee beverages, Coke Zero can be a preferred choice.

Personal Taste Preferences
Some individuals prefer the taste of Coke Zero over other artificially sweetened or sugary beverages. Personal taste preferences play a significant role in beverage choices, and enjoying the taste of a preferred beverage can contribute to overall satisfaction and adherence to dietary choices.
Also Read: Coke Zero Vs Diet Coke: Know The Real Differences!
The Answer to “Is Coke Zero Bad for You?” is…
The answer to is “Coke Zero is bad for you” depends on various factors which are as follows.
Individual Health Considerations
Individuals with phenylketonuria should avoid aspartame-containing products like Coke Zero. For the general population, moderation is key, and those with sensitivities or concerns about artificial sweeteners may choose alternative beverages.
Weight Management Goals
For individuals focused on weight management or reducing calorie intake, Coke Zero can be a suitable alternative to sugary sodas. However, it should not be viewed as a replacement for water or other hydrating beverages.
Dental Health Awareness
While Coke Zero does not contribute to tooth decay directly, the acidity in sodas can erode dental enamel over time. Practicing good dental hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, is crucial.
Caffeine Sensitivity
Coke Zero contains caffeine, which may affect individuals sensitive to caffeine. Managing caffeine intake and being aware of its potential impact on sleep or anxiety is important.
Balanced Diet
Incorporating Coke Zero into an otherwise balanced and varied diet can be acceptable for many individuals. However, relying heavily on artificially sweetened beverages is not a substitute for a nutrient-rich diet.
To Sum Up The Answer…
Is Coke Zero bad for you? The answer lies in moderation and informed decision-making. While Coke Zero can be part of a balanced and varied diet, it should not replace essential sources of hydration like water. For those with concerns about artificial sweeteners or specific health conditions as mentioned above, consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance.
Understanding that individual responses to ingredients vary, it’s essential for consumers to make choices aligned with their health goals and preferences. Coke Zero, like many artificially sweetened beverages, can be enjoyed responsibly as part of a mindful and health-conscious lifestyle. Ultimately, the key to a well-rounded approach to health lies in moderation, informed choices, and a holistic perspective on diet and lifestyle. Hopefully, you got satisfactory answer to the question: “Is Coke Zero bad for you?”. If you really got it then let us know your unfiltered thoughts in the comment section down below. Thanks for visiting and appreciating our work.
