High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a prevalent medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels that persist over time. Hypertension is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other chronic health conditions. That is why, understanding the underlying contributing factors and causes of high blood pressure is essential for effective prevention, diagnosis, and management of this silent life-threatening condition. Here in this article, we have discussed about the 8 potential causes of high blood pressure so that you can get to know how to prevent and manage this condition as soon as possible.
Defining High Blood Pressure
Before delving into the causes of high blood pressure, it’s necessary to clarify what does it mean to have high blood pressure in your body. Actually, blood pressure refers to the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries as it circulates through the body. It is measured using two values: systolic blood pressure (the pressure when the heart contracts) and diastolic blood pressure (the pressure when the heart relaxes between beats). High blood pressure occurs when these values exceed the normal range, typically defined as a systolic pressure of 130 mmHg or higher and/or a diastolic pressure of 80 mmHg or higher.
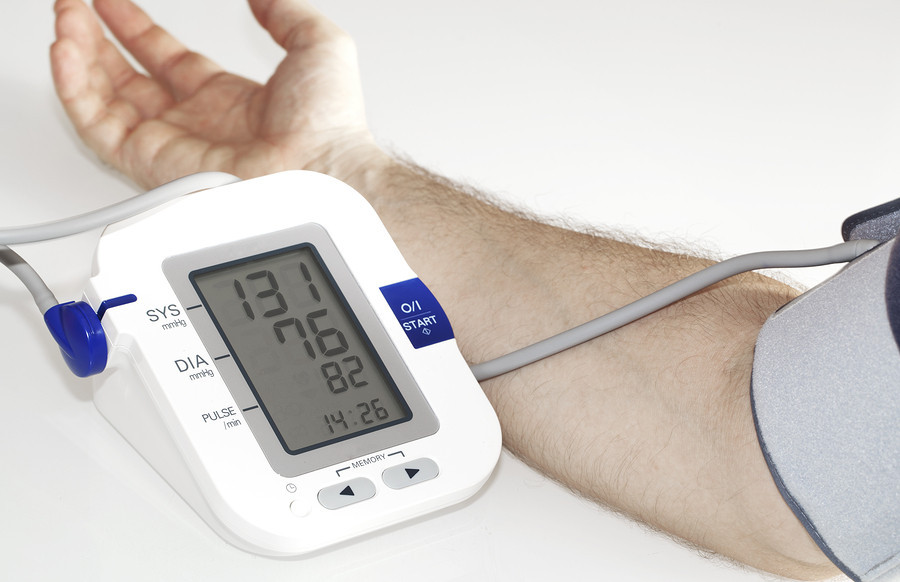
High blood pressure can develop as a result of various genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors and you may notice symptoms of high blood pressure that can help you detect the condition. While the exact cause of hypertension may vary among individuals, the following are common contributors to elevated blood pressure levels. So, without further wasting time, let’s take a detailed look at the potential causes of high blood pressure.
Genetics and Family History
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of high blood pressure. Individuals with a family history of hypertension are at increased risk of developing the condition themselves. Several genetic variants and gene mutations have been implicated in hypertension, affecting mechanisms such as blood vessel function, sodium balance, and hormone regulation. While genetic factors may predispose individuals to hypertension and can be one of the primary causes of high blood pressure, lifestyle factors and environmental influences also play crucial roles in disease manifestation and progression. We also have discussed about this below.
Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle habits can be major contributing factors and causes of high blood pressure. All these modifiable risk factors associated with hypertension are described below.
Poor Diet
A diet high in sodium, saturated fats, refined sugars, and processed foods can contribute to elevated blood pressure levels. Excessive sodium intake can lead to fluid retention and increased vascular volume, raising blood pressure. Diets low in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may also lack essential nutrients such as potassium, magnesium, and fiber, which play key roles in blood pressure regulation.
Sedentary Behavior
Lack of regular physical activity and sedentary behavior are associated with increased risk of hypertension. Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain, reduced cardiovascular fitness, and impaired blood vessel function, contributing to elevated blood pressure levels. Engaging in regular aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises can help lower blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health.

Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption is a risk factor for hypertension and can lead to chronically elevated blood pressure levels. Alcohol affects the central nervous system and cardiovascular system, leading to vasodilation, increased heart rate, and sympathetic nervous system activation. Chronic alcohol abuse can contribute to hypertension, heart disease, and other health complications.

Smoking & Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco use are significant risk factors for hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Nicotine and other harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause vasoconstriction, endothelial dysfunction, and inflammation, leading to increased blood pressure and arterial stiffness. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to second-hand smoke are essential steps in reducing hypertension risk and improving overall health.

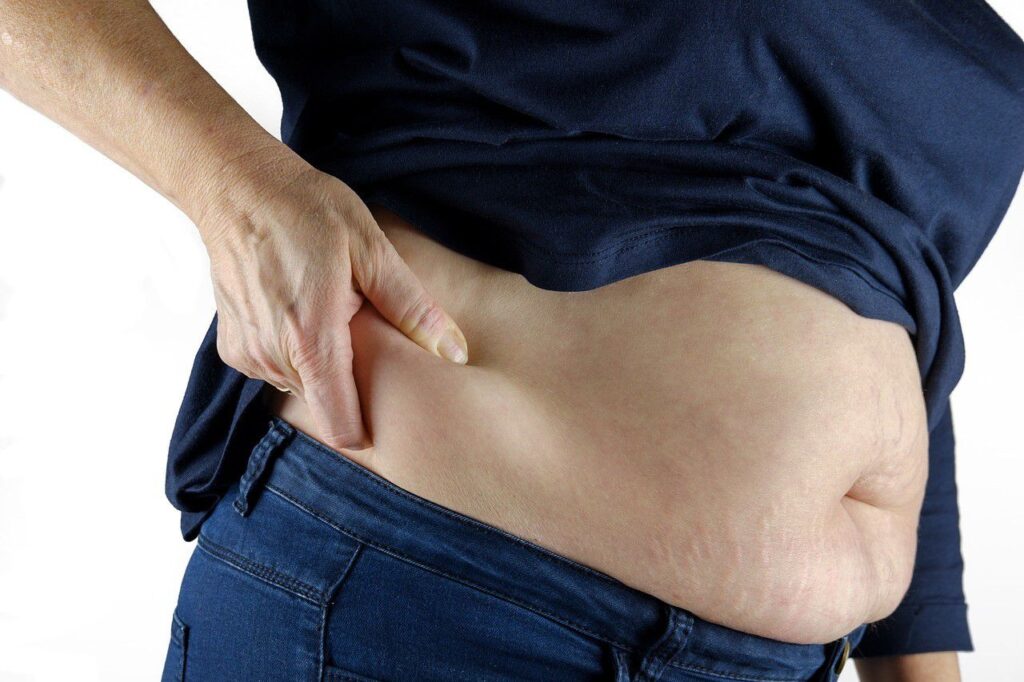
Obesity and Excess Adiposity
Obesity is a major risk factor for hypertension and metabolic dysfunction. Excess adiposity, particularly visceral fat accumulation, is associated with systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hormonal imbalances, all of which are major causes of high blood pressure levels. Adipose tissue releases inflammatory cytokines and adipokines that promote vascular dysfunction and impair blood pressure regulation. Weight loss and weight management strategies are crucial for reducing hypertension risk and improving metabolic health.

Age
Age is a non-modifiable risk factor for hypertension, with blood pressure levels typically increasing with advancing age. Changes in blood vessel structure and function, arterial stiffness, and hormonal regulation contribute to age-related increases in blood pressure. While hypertension is more common in older adults, it can affect individuals of all ages, highlighting the importance of regular blood pressure monitoring and lifestyle modifications for hypertension prevention and management.
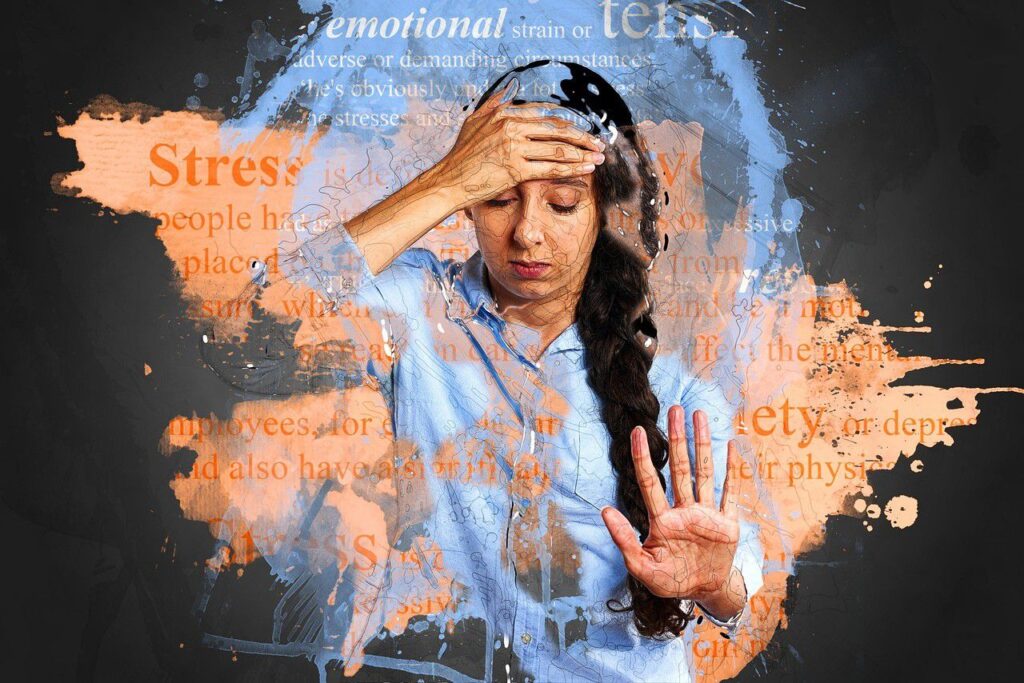
Chronic Stress
Chronic stress and psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and hostility are some of the most common and major causes of high blood pressure levels among middle-aged adults. These psychological factors can contribute to hypertension through activation of the sympathetic nervous system, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and inflammatory pathways. Stress-induced physiological responses, including increased heart rate, vasoconstriction, and cortisol release, can elevate blood pressure levels and contribute to hypertension development. Stress management techniques, relaxation therapies, and behavioral interventions may help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of hypertension and improve overall well-being.

Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity can influence hypertension prevalence and susceptibility. Certain racial and ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Native Americans, have a higher prevalence of hypertension and are at increased risk of hypertension-related complications such as stroke, heart disease, and kidney disease. Genetic factors, socio-economic disparities, cultural influences, and environmental factors contribute to racial and ethnic disparities in hypertension prevalence and outcomes.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can contribute to hypertension by affecting blood vessel tone, fluid balance, and electrolyte regulation. Conditions such as hyperaldosteronism, Cushing’s syndrome, pheochromocytoma, and thyroid disorders can lead to hormonal dysregulation and hypertension. Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy, menopause, and oral contraceptive use can also influence blood pressure levels in women. So, hormonal imbalances are also very common causes of high blood pressure and for this reason, identifying and treating underlying hormonal imbalances is essential for managing hypertension and preventing complications.
Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), insomnia, and restless legs syndrome are associated with hypertension and cardiovascular disease. OSA, characterized by repetitive episodes of upper airway obstruction during sleep, can lead to intermittent hypoxia, sympathetic activation, and endothelial dysfunction, contributing to hypertension and metabolic disturbances. Treating underlying sleep disorders and improving sleep quality are essential for managing hypertension and reducing cardiovascular risk.

Conclusion
As you see, high blood pressure is a complex and multifactorial condition influenced by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors which is why it is crucial to understand the underlying contributors and causes of high blood pressure or hypertension for effective prevention, diagnosis, and management of this silent yet lethal condition. By addressing modifiable risk factors such as unhealthy lifestyle habits, obesity, and chronic stress, individuals can reduce their risk of hypertension and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Regular blood pressure monitoring, healthy lifestyle modifications, and adherence to prescribed treatment regimens are key components of hypertension management and prevention of associated complications. Collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, public health initiatives, and community-based interventions are needed to address the growing burden of hypertension and promote cardiovascular wellness across populations. Hopefully, you found this article about the causes of high blood pressure helpful enough. If you really did then let us know your valuable thoughts in the comments down below. Thanks for visiting and appreciating our work.
