The Mediterranean diet, renowned for its health benefits and culinary delights, has evolved to embrace a new paradigm known as the Green Mediterranean Diet. This innovative approach retains the core principles of the traditional Mediterranean diet while incorporating sustainability and a heightened focus on plant-based foods. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll take a detailed look into the principles, nutritional foundations, health benefits and potential environmental impact of the Green Mediterranean Diet that offers a fresh perspective on healthful eating that aligns with both personal well-being and planetary health.
Principles of the Green Mediterranean Diet
Plant-Centric Emphasis
At the heart of the Green Mediterranean Diet, is a reinforced commitment to plant-based foods. This includes an increased consumption of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. The shift towards a more plant-centric diet not only aligns with health goals but also supports environmental sustainability by reducing the ecological footprint associated with animal agriculture.
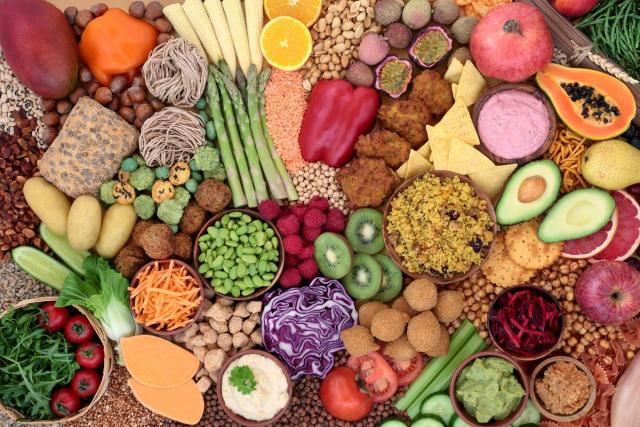

Sustainable Protein Sources
While the traditional Mediterranean diet already includes lean protein sources like fish and poultry, the Green Mediterranean Diet places additional emphasis on sustainable protein alternatives. This may include plant-based proteins such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, and seitan, contributing to reduced environmental impact and a diversified protein intake.
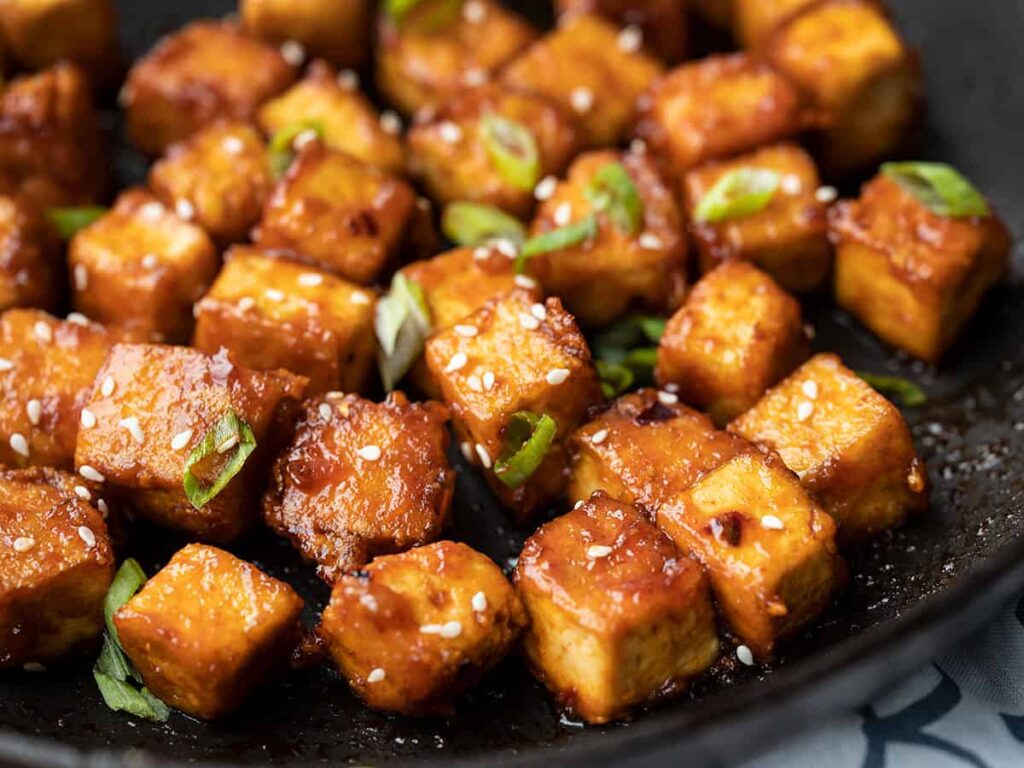

Reduced Animal Products
The Green Mediterranean Diet advocates for a reduction in the consumption of animal products, particularly red and processed meats. This adjustment aligns with both health considerations—reducing saturated fat intake—and environmental concerns related to the resource-intensive nature of meat production.

Locally Sourced and Seasonal Foods
Building on the Mediterranean tradition of valuing locally sourced ingredients, the Green Mediterranean Diet places a heightened emphasis on consuming foods that are in season and sourced locally. This practice supports local farmers, reduces transportation-related carbon emissions, and ensures fresher, more nutrient-dense produce.
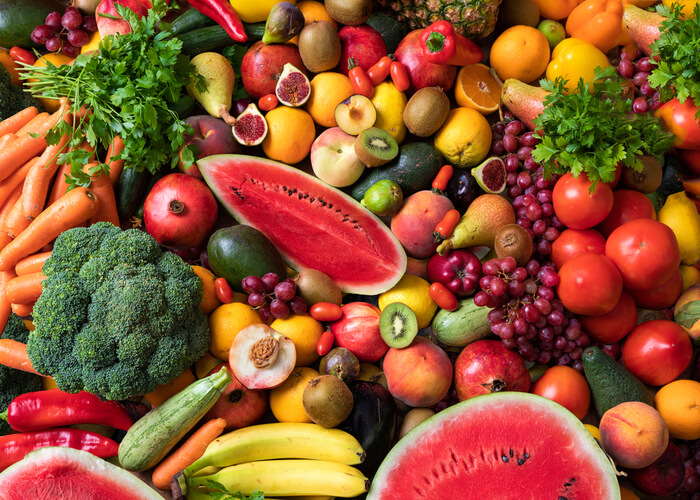

Mindful Food Choices
Mindfulness extends beyond personal well-being to encompass environmental consciousness. The Green Mediterranean Diet encourages individuals to make informed choices about the environmental impact of their food, considering factors such as production methods, transportation, and waste.
Nutritional Foundations
Abundance of Plant-Based Nutrients
The increased focus on plant-based foods ensures a diverse intake of essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. These nutrients contribute to overall health and may offer protective effects against chronic diseases.
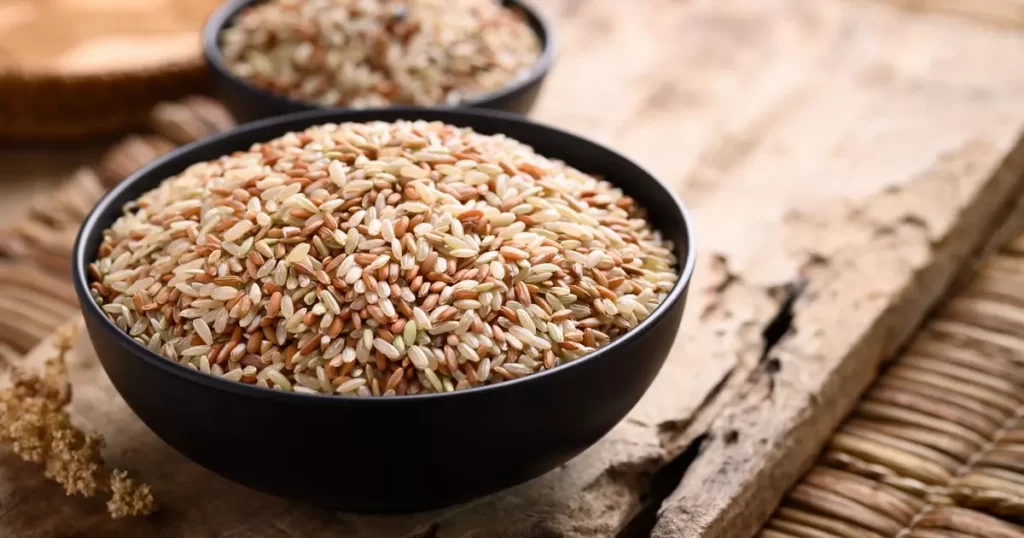

Whole grains such as quinoa, farro, and brown rice provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and various micronutrients. They are staples in the Green Mediterranean Diet, supporting sustained energy and digestive health.
Sustainable Plant-based Proteins
Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich sources of plant-based protein, fiber, and various nutrients. Integrating legumes into the diet contributes to protein needs while reducing reliance on animal products. In addition, almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds offer healthy fats, protein, and essential nutrients. These foods are not only nutritionally dense but also environmentally sustainable.
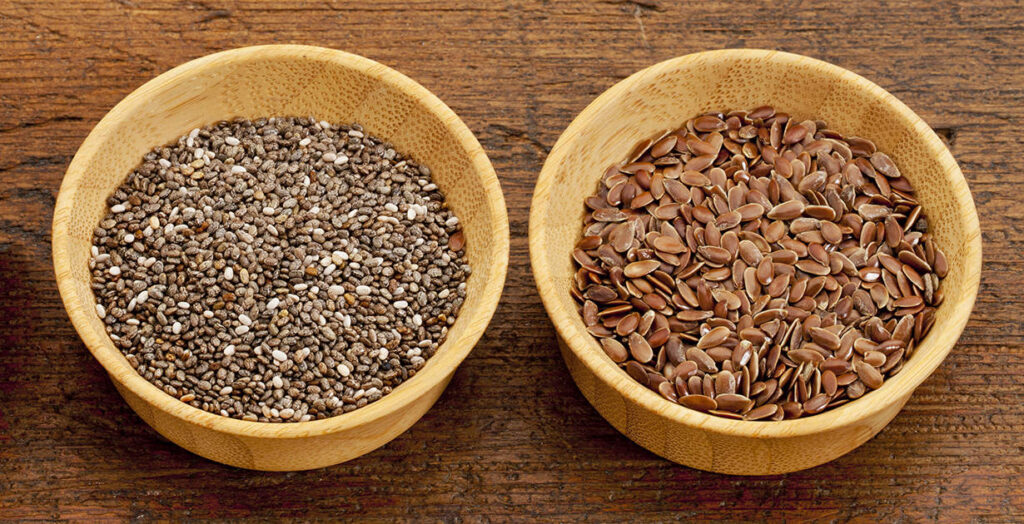

Plant-Based Fats
Maintaining its central role, olive oil provides monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. Its use in cooking and as a salad dressing aligns with heart health and sustainable dietary choices.
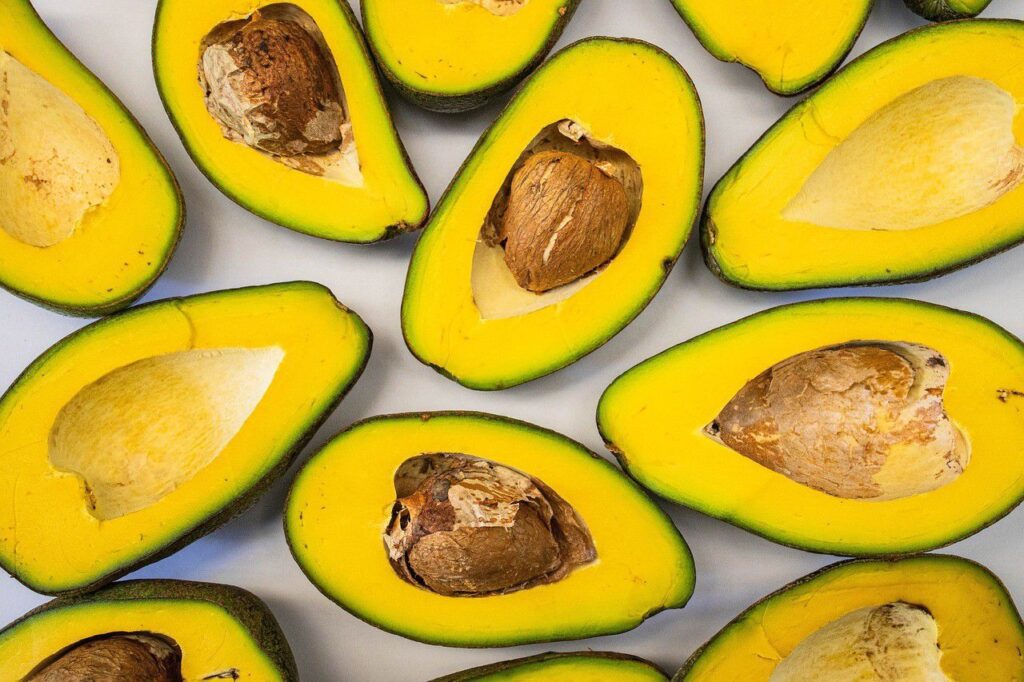

Rich in monounsaturated fats and various vitamins, avocados are a nutritious addition to this type of Diet. They contribute to satiety and enhance the flavor and texture of meals.
Lean Animal Proteins
While the emphasis is on plant-based sources, the Green Mediterranean Diet retains the inclusion of fish and seafood, particularly varieties rich in omega-3 fatty acids. This aligns with both health benefits and sustainable fishing practices. Moreover, lean poultry remains a part of the diet, contributing to protein needs with a lower environmental impact compared to red meat.

Health Benefits of the Green Mediterranean Diet
Heart Health
The emphasis on plant-based fats, particularly from olive oil, and the inclusion of omega-3-rich fish contribute to cardiovascular health. The Green Mediterranean Diet’s focus on reducing saturated fat from animal products aligns with heart-protective goals.

Weight Management and Metabolic Health
The diet’s abundant fiber content, derived from whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, supports weight management and metabolic health. Plant-based proteins contribute to satiety, potentially reducing overall calorie intake.

Reduced Cancer Risk
The Green Mediterranean Diet’s emphasis on antioxidant-rich foods, along with a reduction in red and processed meat consumption, may contribute to a lower risk of certain cancers. Phytochemicals and bioactive compounds found in plant foods have been linked to protective effects.

Diabetes Prevention
The diet’s focus on complex carbohydrates, fiber-rich foods, and a reduction in processed sugars align with strategies for preventing type 2 diabetes. Plant-based proteins contribute to improved insulin sensitivity.
Environmental Impact
Reduced Carbon Footprint
The Green Mediterranean Diet addresses concerns about the carbon footprint associated with traditional diets high in red and processed meats. By promoting plant-centric meals and sustainable protein sources, individuals can actively reduce their environmental impact.
Preservation of Biodiversity
A diet rich in plant-based foods, sourced locally and in season, contributes to the preservation of biodiversity. Reduced reliance on intensive animal farming practices supports ecosystems and reduces the strain on natural resources.
Water Conservation
Animal agriculture is known to be water-intensive. Shifting towards a diet with a greater emphasis on plant-based foods reduces water consumption, contributing to water conservation efforts.

Support for Sustainable Agriculture
Embracing locally sourced and seasonal produce fosters support for sustainable agriculture. This encourages farming practices that prioritize soil health, reduce the need for synthetic inputs, and promote ecosystem resilience.
Conclusion
The Green Mediterranean Diet represents a harmonious fusion of tradition, health consciousness, and environmental sustainability. By infusing the time-tested principles of the Mediterranean diet with a plant-centric and sustainable ethos, individuals can embark on a culinary journey that not only nurtures personal well-being but also contributes to the health of the planet. As we navigate a world where dietary choices impact both individual health and global sustainability, the Green Mediterranean Diet emerges as a beacon of balance, offering a pathway to a delicious and healthy living that resonates with both the present and the future of us as well as our planet. Hopefully, you found this article helpful enough. If you really did then let us know your valuable thoughts in the comment section down below. Thanks for visiting and appreciating our work.
