Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition characterized by the body’s reduced responsiveness to the hormone insulin, resulting in impaired glucose regulation and elevated blood sugar levels. This condition is a key precursor to type 2 diabetes and is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and other chronic health conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for insulin resistance is essential for effective management and prevention of associated complications. Let’s know all the details about it.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a central role in regulating blood sugar levels and facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy production. In individuals with this type of health issue, cells become less responsive to the action of insulin, requiring higher levels of insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. This compensatory response can lead to hyperinsulinemia, or elevated insulin levels, as the pancreas produces more insulin in an attempt to overcome the resistance.
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
This condition often develops gradually over time and may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience a range of symptoms which are described below.
Elevated Blood Sugar Levels
One of the hallmark signs of insulin resistance is consistently high blood sugar levels, known as hyperglycemia. This occurs when cells are unable to efficiently uptake glucose from the bloodstream, leading to glucose accumulation in the blood. Symptoms of hyperglycemia may include increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.

Weight Gain and Obesity
Insulin resistance is closely associated with obesity and excess adiposity, particularly abdominal or visceral fat accumulation. Adipose tissue, or fat cells, release inflammatory cytokines and hormones that can disrupt insulin signaling and contribute to this issue. Individuals with this health issue may experience unexplained weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, despite efforts to maintain a healthy diet and exercise regimen.

Fatigue and Lethargy
Changes in energy metabolism associated with this condition can lead to feelings of fatigue, lethargy, and reduced physical stamina. As cells become less efficient at utilizing glucose for energy production, individuals may experience fluctuations in energy levels throughout the day, with periods of fatigue and decreased motivation.

Increased Hunger and Cravings
Insulin resistance can disrupt appetite regulation and lead to increased feelings of hunger and cravings, particularly for high-carbohydrate and high-calorie foods. This may be due to fluctuations in blood sugar levels and dysregulation of hunger hormones such as leptin and ghrelin, which play a role in appetite control.

Skin Changes
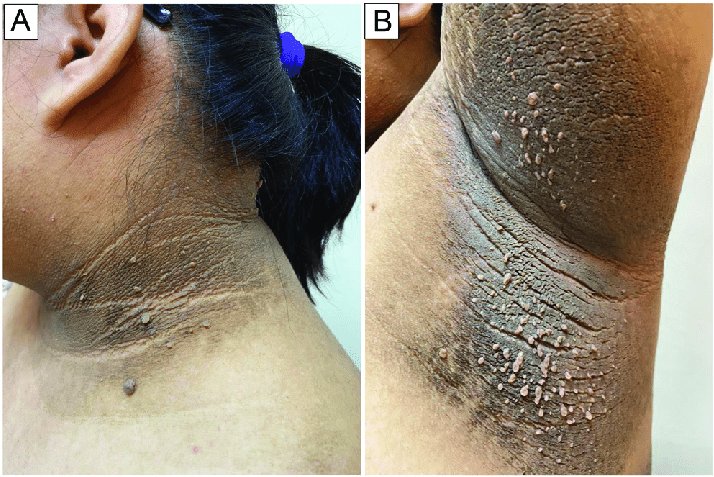
Skin manifestations from this health condition may include acanthosis nigricans, a condition characterized by dark, velvety patches of skin, typically occurring in areas of friction or folds, such as the neck, armpits, and groin. These skin changes are thought to be related to insulin-induced hyperpigmentation and may serve as a visible marker of insulin resistance.
Also Read: 10 Benefits of Aloe Vera on Skin!
High Blood Pressure
This health issue is also associated with an increased risk of hypertension, or high blood pressure, due to alterations in vascular function and sodium retention. Elevated insulin levels can lead to vasoconstriction, or narrowing of blood vessels, and promote sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, contributing to hypertension and cardiovascular complications.
Causes of Insulin Resistance
Several factors contribute to the development of this health issue, including genetic predisposition, lifestyle factors, and underlying medical conditions. The primary causes of this problem include:
Genetic Factors
Genetic susceptibility plays a significant role in the development of this health issue and type 2 diabetes. Certain genetic variants can affect insulin sensitivity, glucose metabolism, and adipose tissue function, increasing the risk of insulin resistance in predisposed individuals.
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle
Excess adiposity, particularly visceral fat accumulation, is a major risk factor for insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction. Obesity-related inflammation, adipokine dysregulation, and lipid accumulation in peripheral tissues can impair insulin signaling and contribute to this health issue. Sedentary behavior and lack of regular physical activity further exacerbate these metabolic abnormalities and increase the risk of this health problem.
Don’t Miss: 10 Best Cardio for Weight Loss!
Poor Diet
Dietary factors play a crucial role in the development of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. A diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and saturated fats can lead to dyslipidemia, oxidative stress, and inflammation, contributing to health problems like this and impaired glucose metabolism. Processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive calorie intake can also promote weight gain and exacerbate this type of health issue.
Aging
Aging is associated with alterations in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, contributing to an increased risk of this health trouble and type 2 diabetes in older adults. Age-related changes in adipose tissue distribution, mitochondrial function, and hormonal regulation can impair insulin signaling and glucose uptake, leading to insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal factors, including cortisol, growth hormone, and thyroid hormones, can influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Dysregulation of these hormones, as seen in conditions such as Cushing’s syndrome, acromegaly, and hypothyroidism, can lead to insulin resistance and metabolic disturbances.
Sleep Disorders
Sleep disturbances, including sleep apnea, insomnia, and circadian rhythm disruptions, are associated with this health condition and metabolic dysfunction. Inadequate sleep duration and quality can impair glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity, and appetite regulation, increasing the risk of this health problem and type 2 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Best Magnesium for Sleep: A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosis of Insulin Resistance
Diagnosing this health issue typically involves a combination of clinical assessment, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Common diagnostic tests for it are as follows.
Fasting Blood Glucose Test
A fasting blood glucose test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast and is used to screen for hyperglycemia and impaired glucose tolerance, both of which are indicative of this condition.

Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
An oral glucose tolerance test involves consuming a standardized glucose solution and measuring blood sugar levels at regular intervals to assess the body’s ability to metabolize glucose. Elevated blood glucose levels during the test may indicate insulin resistance or impaired glucose tolerance.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test
The hemoglobin A1c test measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months and is used to assess long-term glycemic control. Elevated HbA1c levels may indicate insulin resistance and an increased risk of diabetes-related complications.
Insulin Sensitivity Tests
Insulin sensitivity tests, such as the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp and the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), directly measure the body’s response to insulin and are used to diagnose the issue and assess metabolic health.
Treatment of Insulin Resistance
The management of this health problem focuses on lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy, and targeted interventions to improve insulin sensitivity and metabolic health. Treatment strategies for it are described below with details.
Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary changes, regular exercise, and weight management are cornerstones of insulin resistance management. Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar levels, promote weight loss, and improve insulin sensitivity. Regular physical activity, including aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises, can enhance glucose uptake, reduce this health problem, and support overall metabolic health.

Don’t Miss: Keto Diet Plan: Foods to Eat, Meal Plans & Tips for Ketosis!
Medications
Pharmacotherapy may be recommended to manage insulin resistance and associated comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Commonly prescribed medications for this health issue include metformin, thiazolidinediones (TZDs), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. These medications work by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing hepatic glucose production, and enhancing glucose uptake in peripheral tissues.
Insulin Therapy
In cases of severe insulin resistance or advanced type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary to achieve optimal glycemic control and prevent complications. Insulin therapy involves administering exogenous insulin via injections or insulin pumps to regulate blood sugar levels and overcome it.
Weight Loss Surgery
Bariatric surgery may be considered for individuals with severe obesity and insulin resistance who have failed to achieve adequate weight loss with lifestyle modifications and medications. Procedures such as gastric bypass surgery and sleeve gastrectomy can lead to significant weight loss, improvement in insulin sensitivity, and resolution of type 2 diabetes in some cases.
Management of Comorbidities
Addressing underlying medical conditions and comorbidities associated with insulin resistance, such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and sleep disorders, is essential for comprehensive management and prevention of complications. Medications, lifestyle modifications, and targeted interventions may be recommended to control comorbidities and optimize metabolic health.
The Sum-up
Insulin resistance is a common metabolic disorder characterized by reduced responsiveness to insulin and impaired glucose regulation. Left untreated, this health issue can progress to type 2 diabetes and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and other chronic health conditions.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of insulin resistance, understanding its causes, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies are essential for effective management and prevention of associated complications. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, optimizing weight management, and addressing underlying medical conditions, individuals with this health condition can improve insulin sensitivity, stabilize blood sugar levels, and enhance overall metabolic health. Consultation with a healthcare provider or endocrinologist is recommended for comprehensive evaluation, diagnosis, and management of this issue and its associated metabolic disorders. Hopefully, you found this article helpful enough. If you really did then let us know your valuable thoughts the comments down below. Thanks for visiting and appreciating our work.
